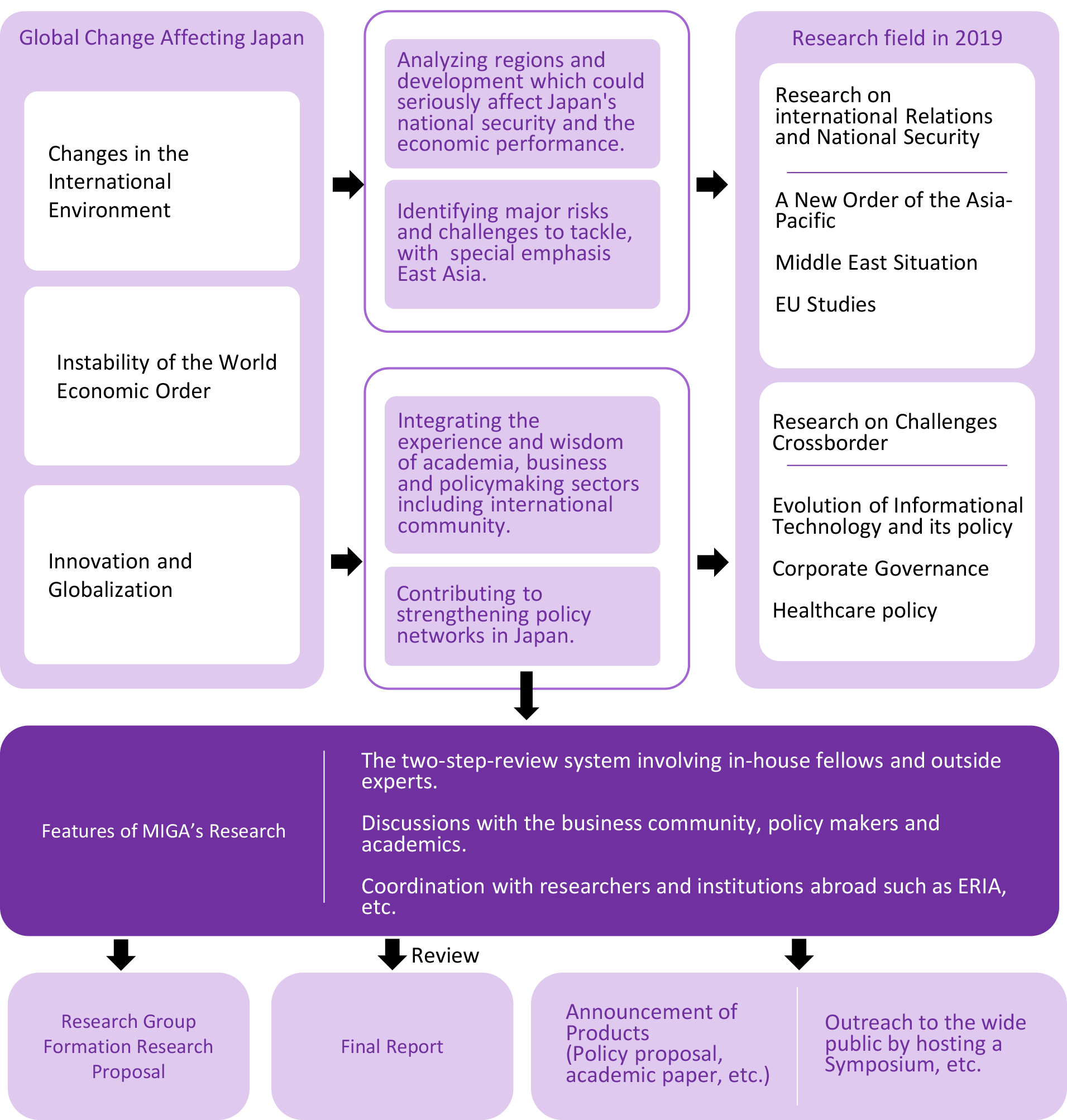
RESEARCH OVERVIEW
International Relations
Asia-Pacific
Research on the indo-Pacific Strategy and the Belt and Road initiative
The objective of this research is to examine what kind of governance framework would evolve in the Asia-Pacific region (Indo-Pacific region) in the future under the relative decline of the United States and the rise of China, and how the role of Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy (FOIP) would play in it.
The question that needs to be kept in mind while examining the future of governance in the Asia-Pacific region (Indo-Pacific region) is how countries with power like the United States, China, India, Japan, Russia, and Indonesia can develop a cooperative framework to make decisions smoothly: rather than assuming a unilateral framework created by a single hegemonic power.
In this research, BRI and FOIP will be analyzed from three perspectives. First, this research intends to clarify what BRI is truly about by examining the actual investment projects. Since BRI is principally an economic cooperation initiative, the progress and results of individual projects, especially infrastructure projects, can be evaluated based on various economic data. The evaluation will also include the BRI’s degree of contribution to the recipient countries’ economic growth and their economic relations with China, as well as the BRI’s long-term implication for China’s national finance.
The second perspective is the possibility of cooperative relations between BRI and FOIP. Considering the regional diversity and huge demand for infrastructure development in Asia in conjunction with the fact that both BRI and FOIP are still nothing but policy concepts at this stage, there still is room for BRI and FOIP to avoid confrontational path. The question is what kind of interface (or common ground) can be developed to foster cooperative relations between the two concepts. The research will explore some keywords, like "connectivity", to analyze the possibility of cooperative relations.
The third perspective is how Japan, a neighbor of China and the ally of the United States, would contribute to the development of governance in the Asia-Pacific region (Indo-Pacific region). This research will analyze the positive and negative implications of BRI and FOIP for the Japanese economy/ companies, diplomacy, and national security to examine the policy challenges Japan faces due to long-term structural changes and short-term risk fluctuation.
Middle East
In this project, we analyze the social situation and the latest trends in the Middle East region, which is still in turmoil after the de facto disappearance of so called “ Islamic State”. Another important axis of our analysis is on the US-Russian relationship, after the birth of the new President of Trump, over Iran, Syria and Turkey, Afro-Middle Eastern relationship, and Eurasian political dynamics and the transformation of social structure, extending from the Gulf States, Israel, and the Maghreb countries to the Caucasus and Central Asia region. In academic year 2018-2019, we examined the dynamism of the international situation, focusing on the US policy toward Middle East, the Turkish domestic power struggle that holds the key to Syria's situation, and the new Syrian peace process led by Russia, Iran, and Turkey. Our main interest in 2019-2020 is to analyze the regional situation around Syria, the transformation of the international order focusing on Iran, Israel and Saudi Arabia, and the relationship between the EU in the middle of Brexit and the Middle East focusing on France, Morocco and Gibraltar. In addition, field surveys in Indonesia and Brunei are to be conducted to examine the impact on Asia after the collapse of IS territory in Syria.
EU
Confusions over the European Union (EU) continues. This project, however, aims to provide comprehensive research and analysis on various issues surrounding the EU without being overly pessimistic.
Firstly, the UK's withdrawal from the EU (Brexit) and its implications continue to be one of the research questions. Prime Minister May, who had been taking the lead on Brexit, has been forced to resign now. If a Brexit hardliner becomes the next prime minister, the risk of “no-deal Brexit” will increase. On the other hand, there is an increasing momentum towards “Breturn” (EU return) among the British people that maintains the possibility of a second referendum. One way or the other, the Brexit confusion will inevitably divide the UK. In this research, the implications of Brexit for the UK, EU, and the world economy will be analyzed from short and long-term perspectives.
Secondly, analyzing the development of growing Euroscepticism continues to be one of the critical themes. The European Parliament election in May was a major touchstone for evaluating the depth of populism in the EU. While the rise of ultra-rightists and the decline of centrists parties was prominent, with the expansion of liberal and environmentalist groups, the pro-EU parties have maintained a majority. However, since the disparities among the EU is widening, keeping track of the Eurosceptics trend is critical.
Thirdly, this research will also analyze the question of how the powers of Germany and France, who had led the EU integration will change. As Chancellor Merkel steps down from party leadership and President Macron continues to face prolonged anti-government protests, both leaders have been weakened. Against this backdrop, how Germany and France can reinvent the German and French-led EU system is an ongoing question. Appointments for major EU posts such as the Presidents of the EU Commission and the European Central Bank will also determine the future of the EU.
The EU faces various challenges. The Eurozone economy is slowing down and the New Cold War between the U.S. and China is weighing down the overall EU economy. However, the significance of the EU as an advocate for free trade would increase as the protectionist policies of President Trump drag down the world economy.
Economy and Society
Information
Activation of Digital Business Creation
Digital technology, which has been a tool for efficiency, has changed to a weapon to create a new business (digital business) by the progress of exponential technology.By the end of last year, we have been working on the present state and prospects of digital business from multiple perspectives (venture companies, large-scale enterprises, and Chinese companies that show rapid growth in recent years)Based on the results obtained from these research activities, in fiscal 2019, we would like to discuss measures to stimulate the creation of digital business in Japan.
Specifically, the following tasks are assumed.
・Organize the differences between digital business and general business.
・Analysis of the success factors for digital business, which can be read from domestic and overseas cases.
・Consideration of measures to promote digital business based on Japan's industrial structure and corporate structure
The research results are expected to eventually be compiled as concrete proposals
Cybersecurity, commonly defined as collective defense against any form of malicious attack exploiting network computer vulnerabilities, is recognized as a buzz word in our society today. The term emerges from a complex system of digital communication infrastructure, which accelerates the innovation of internet communication technology for effective transaction and distribution on one hand, and induces the incident of cyberattacks that will result in personal information leakages, data manipulations, denial of services and so on..
In overseas, cyberattacks are seen elsewhere and the attackers choose indiscriminately their targets regardless of national government, private institutions, public service, or infrastructure facilities. Such representatives of recent cyberattacks can be exemplified as STUXNET (a secret hacking spyware invented by US and Israel military intelligence in an attempt to destroy uranium reactors suspected of preserving nuclear weapons in 2010), Ukraine cyber attacks on an electric power grid, and Russian intervention into 2016 US national election (unanimous hackers working closely with a Russian internet company hacked into the DNC e-mail server and disclosed John Podesta’s(Clinton’s then campaign strategist) private e-mails dumped into the WikiLeaks).
What becomes clear in recent trend is an increasing deceptiveness and preciseness of cyberattack in general. WannaCry, a refined ransomeware that stunned the world in May 2017, is believed to be a common product that became widely available to those involving in engineering the exploits that were re-designed from previous malware and spyware programs. A notorious illegal trading website such as Dark Webs have also provided a key distribution channel to these online dealers across the border. Subsequently, it opened the floodgate for a threat of ransomeware attack spreading across the border and business fields. WannaCry outbreak was followed by its successors, Petya and NotPetya, respectively. They continued to strike the fear into the heart of private corporations and national governments.
Japan took its first major step to establish national cybersecurity policy, led by a data breach incident occurred at the website of Public Pension Service in June 2013. Since the Basic Cybersecurity Law was passed in November 2014, the national government worked energetically with foreign countries to provide effective analysis and monitoring mechanism of cyberthreats and hands-on training to public and private sectors. Fortunately or not, people in Japan have not seen any remarkable incident that would cause a catastrophic injury to national infrastructure or corporate interest (such as attacks on electric power grid, water resource facility, or a giant supermarket chain) so far. However, witnessing its far-flung effect into domestic soil (news of a teenage boy arrested for using the software to steal money), the nation found that the Wanna Cry pandemonium was compelling enough to take its risk seriously and urged for continuous investment in security policy at both government and civilian level. Still, Japan’s security policy faced numerous challenges: 1) consolidating discrete governing bodies of cybersecurity for effective policy-making decision; 2) developing educational programs across the academic and tertiary institutions; 3) budget constraint; and 4) need for experienced professionals, specialists, and administrators who can discern the practice of cybersecurity from crisis communication perspective. Particularly, a thorny issue is that practice of security personnel training is highly constrained into domestic industrial structure. It would come as no surprise to see training methodology and prospect for career-path as a hot topic.
In spite of such complex culture of challenges, Japan is receiving a strong request from ASEANS reading intellectual capacity and expertise. Cybersecurity is an interdisciplinary field that consists of legal and political frameworks and solid input from the practice of information analysis and network infrastructure. Our research focuses on the ongoing security trend in business enterprises and policy practice at national/international level. Particularly, we are thinking of addressing the issues focusing on IoT and information sharing system, by collaborating with business leaders and policy makers from domestic and overseas, as well as working closely with academia and industrial clique. As our ultimate goal, we are seeking an initiative for sound advice to policy makers on security professional training and related policy practice, and propose open campus lectures at university campus as well.
Corporate Governance
Analysis of the Status and Issues of Implementation and Operation of Corporate Governance Reform
The Corporate Governance of listed companies in Japan made a substantial progress through the Stewardship Code, the revision of company law and the Corporate Governance Code introduced during the years 2014-2015. This project analyzes whether the general principles requested by the Corporate Governance Code such as strategy for the sustainable growth of corporate value enhancing capital efficiency,securing the rights of shareholders, fulfillment of the responsibility of the board,appropriate disclosure, dialogue with shareholders, etc. are complied with and performed by companies not as forms but as matter of substance including change of the mindset of corporate top management. The project also aims to review the new trend of the corporate governance issues in Europe and USA. The members of study group are the intellect from diversified background such as academia, industry, government, legal circle, etc.
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A), from the standpoint of both buyers and sellers, have become more familiar to Japanese companies. As background for this trend, there are the declining population in Japanese society and large changes to its industrial structure. For that reason, (1) M&A from the buyer’s perspective is now crucial for the survival of Japanese companies. At the same time, (2) the number of Japanese companies that are the objects of M&A (i.e., receive an offer of purchase) will also increase hereafter. This study group, when considering the use of M&A by Japanese companies, will examine the changes in M&A by Japanese companies over the last 10-15 years both quantitatively and qualitatively, and based on our understanding of current conditions will discuss the desirable direction of M&A hereafter, with the goal of providing recommendations by the study group.
Health/Healthcare
In this research, this unit revisits concepts of “health” which has been thought as a given by health policies, and aims to find basic values of health policies and trends of corporate activities. Environment around health policies is rapidly changing. This unit previously had researches on health systems as infrastructures of healthcare, trends of global corporate activities on marketing pharmaceuticals and medical devices, and trends of providers of health services including hospitals and governments, especially Ministries of Health. Those researches found the concepts of health itself is being transformed and goals and targets of health policies must be changed gradually, though almost all have thought the model of cure of patients with diseases as a fundamental value for health policies. In FY2019, this unit tries to make useful reports for medical or health companies in considering future strategies for realizing innovations. The reports could be rerated with (1) Trends and actions of main authorities in the world of health policies, including ASEAN member states, and (2) interviews with global companies. In FY2019, the unit makes use of opportunities, including on site visit researches at institutions such as Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy etc., academic conferences, discussion tables or joint sessions if necessary at University of Tokyo/Japan Society for the Promotion of Machine Industry.
Since the Abe Cabinet specified healthcare and medical development as one of the major focuses of the administration, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, provisionally introduced a new pricing system in 2016 for medical technologies based on cost-effectiveness evaluation. One of the challenges is a method for pricing to reflect the goodness of cost-effectiveness. Hence this project critically appraises the pricing method, which is proposed by Chuikyo in the institutionalization of cost-effectiveness evaluation in April 2019, and holds an international symposium to compare and discuss the issues relevant to the method in UK and France.